- 18 5 月, 2011
- 1956 Views
- Media, Press Release
Diagnosis and Treatment of Voice Problems Using a Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine Approaches
The Voice Research Laboratory of the Faculty of Education, HKU has investigated the voice problems in 205 patients (Year 2005 – Year 2010) using both the traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine (speech therapy) approaches. About 2/3 (62.4%) of the patients were diagnosed with “yin xu” (yin deficiency). The symptoms of “yin xu” (yin deficiency), manifests as hoarseness of voice, dryness of the mouth and throat, feverish sensation of palms and soles, night sweating, insomnia, and dry stool. These symptoms are consistent with the “dehydration” condition, which is seen as a major risk factor and condition for developing voice problems in western medicine.
Voice Problems Investigation
Total cases collected is 205, period is 5 years (2005-2010), aged from 10 to 78 years old. There are 64 male and 141 female patients.
Zang-fu / Organs & TCM View of Water and Qi Regulation
Zang-fu is not simply anatomical organs. It represents the TCM view of generalization of the physiology and pathology of human body systems; Lung dominates Qi and controls respiration. It also regulates water passage and is related to distribution of Qi and fluid to Zang-fu organs; Spleen governs transportation and transformation of water and nutrients; Kidney controls water metabolism and receives Qi assisting in respiration; Liver regulates bodily Qi and harmonizes the emotions.
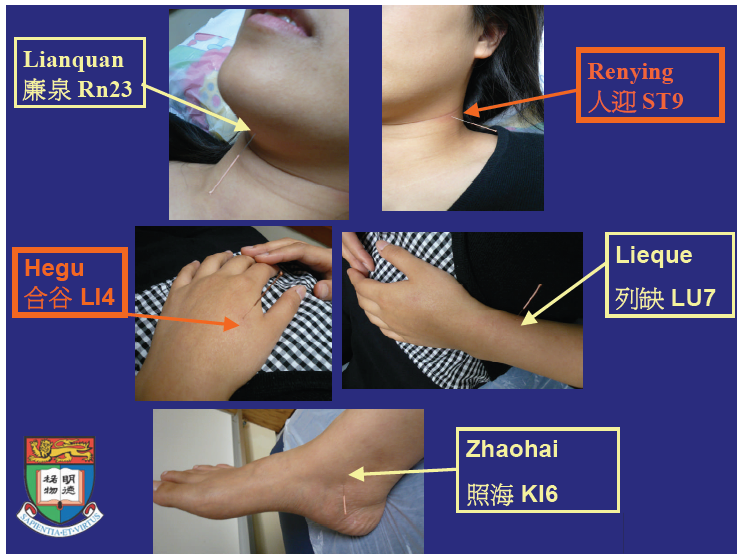
Acupuncture points for treatment
Renying (St9), Lianquan (Rn23), Lieque (Lu7), Hegu (Li4), Zhaohai (Ki6). Bilateral acu points, 9 points in total.
Nourishing Yin Herbs
Yang Yin Qing Fei Tang Decoction includes Radix Rehmanniae, Radix Ophiopogonis, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., Radix Scrophulariae, Bulbus Fritillariae Cirrhosae, Cortex Moutan, Menthahaplocalyx Briq., Radix Paeoniae Alba. This decoction nourishes Yin and clears the lungs, cools blood and removes toxicity.
Acupuncture treatment 138 cases
Zang-fu symptoms:
Liver – 30 (PRE); 6 (POST)
Spleen – 26 (PRE); 1 (POST)
Lung – 35 (PRE); 0 (POST)
Kidney – 30 (PRE); 4 (POST)
Xue / deficiency symptoms:
Qi xue – 73 (PRE); 2 (POST)
Yin xu – 91 (PRE); 4 (POST)
Herbal medicine treatment 18 cases
Zang-fu symptoms:
Liver – 2 (PRE); 2 (POST)
Spleen – 8 (PRE); 5 (POST)
Lung – 3 (PRE); 3 (POST)
Kidney – 5 (PRE); 2 (POST)
Xue / deficiency symptoms:
Qi xue – 11 (PRE); 8 (POST)
Yin xu – 9 (PRE); 6 (POST)
Acupuncture & Herbal medicine treatment 49 cases
Zang-fu symptoms:
Liver – 17 (PRE); 8 (POST)
Spleen – 17 (PRE); 10 (POST)
Lung – 11 (PRE); 1 (POST)
Kidney – 10 (PRE); 7 (POST)
Xue / deficiency symptoms:
Qi xue – 22 (PRE); 12 (POST)
Yin xu – 28 (PRE); 10 (POST)
Conclusion
In summary, in patients who were suitable to receive acupuncture, the Zang-fu symptoms and deficiency symptoms greatly reduced after the treatment. In patients who were not suitable to receive acupuncture and were given herbal medicine, the Zang-fu symptoms and deficiency symptoms only reduced slightly after the treatment. In patients who were more severe and had to receive both acupuncture and herbal medicine, the Zang-fu symptoms and deficiency symptoms reduced by approximately half after the treatment.